Tiny Spheres, Big Impact: Unraveling the World of 1μm Microspheres in PMMA and Polystyrene
Microspheres, the tiny wonders that measure just 1 mm (micrometer) in size, have a crucial role to play in a variety of industrial and scientific applications. We'll take a trip to discover the fascinating microcosmic world by exploring their distinct characteristics as well as the many fields in which they can be utilized in practical ways.
Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Microspheres:
Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Microspheres also known as PMMA in short, can be described as transparent thermoplastic polymer renowned by its clarity in the light and exceptional weather-proofing. If miniaturized into Polystyrene Microspheres 1μm, they reveal amazing features:
optical clarity:
PMMA microspheres retain the exceptional transparency of polymers, which makes them ideal for applications such as microscopy or particle tracking that require clarity.
Sphericity: The microspheres in HTML0 are well-known for their superior amount of sphericity. This ensures consistency and accuracy in many uses, such as to calibrate standards as well as in biomedical research.
Chemical inertness: PMMA microspheres showcase their chemical inertness and are suitable for use with a variety of chemical solvents. This feature makes them better suited for various analyses and experiments.
Polystyrene Microspheres 1mm:
Polystyrene is one of the synthetic polymers, joins the microsphere thanks to its unique properties:
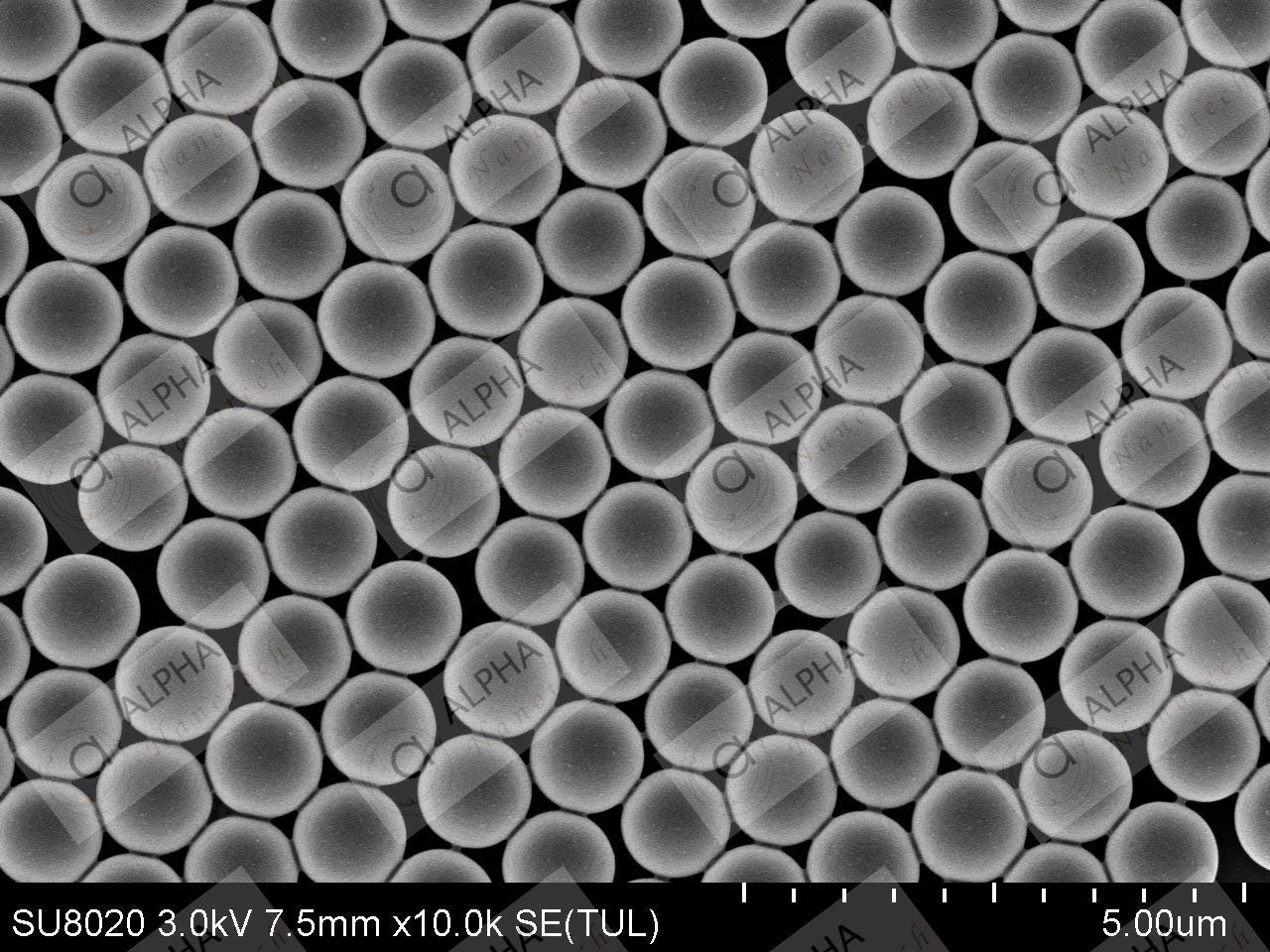
Polystyrene Microspheres 1μm
Uniform Size:
The Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Microspheres are recognized because of their uniform size important in fields like diagnostics and flow cytometry when precision is crucial.
Surface Modification: Microspheres made of polystyrene offer an easy surface modification which allows researchers to customize the properties of their materials for particular applications for example, like carrying out protein binding tests, or carrying out cellular research.
Electrostatic Property: It's not unusual to find polystyrene microspheres exhibiting electrostatic charges. This interesting property could be exploited for applications such as photocopiers that print toner as well as carriers for drugs delivery systems.
Conclusion:
Poly(Methyl Methacrylate) Microspheres and Polystyrene Microspheres 1μm might seem small however their impact is felt in a significant way across industrial and scientific fields. Their remarkable properties, versatility and wide range of applications keep growing, and establishing the microspheres as essential devices for scientists and engineers. While we explore the capabilities of these marvels in microspheres, we are able to explore an area of accuracy as well as clarity and creativity which drives advancement in many areas.



